Highlights About the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA)
- Sonia Lee
- Aug 25, 2025
- 6 min read
Date: August 7, 2025
By: Sonia Lee Ng, CPA
This Bill was signed into law on July 4th, 2025. Public Law 119-21

Disclaimer
The information provided in this post is for general information purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional tax, legal, or financial advice. You should consult with a qualified tax professional or CPA regarding your specific situation before making any tax-related decisions.
Highlights
Summarize of the provisions impacting individuals, estates, businesses and in general
Individuals
Permanent Tax Relief
Permanent Tax Relief
Tax Brackets: The Tax Brackets introduced in 2017 by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act are now permanent.

Tax brackets for 2025 under the One Big Beautiful Bill Act: differing rates for Single and Married Filing Jointly statuses ranging from 10% to 37%. Standard Deduction 2025: Single $15,750, Head of Household $23,625, Married Filing Jointly $31,500.

Standard Deduction 2025
Temporary Tax Relief
Temporary Deductions (2025-2028)
The State and Local Tax (SALT) Deduction Increase: (2025-2029)
-Maximum annual deduction: $40,000 in 2025 (1% indexed annually)
-In year 2030, it reverts to $10,000.
-Phase-Out begins at AGI>$500,000 for 2025. A 30% reduction on excess.
No tax on Tips (2025-2028) for employees and self-employed:
-Maximum annual deduction of up to $25,000
-Phase-Out begins at MAGI>$150,000 (Single), >$300,000 (Joint)
-Must be -reported in a form W-2, 1099, or other statement
No Tax on overtime compensation (2025-2028):
-Maximum -Annual deduction $12,000 (Single), $25,000 (Joint).
-Phase-Out: MAGI>$150,000 (Single), >$300,000 (Joint)
No tax on Car Loan Interest:
-Maximum annual deduction: $10,000
-Interest paid on a loan originated after 12/31/2024, used to purchased a qualified vehicle assembled in the U.S. for personal use.
-Phase Out: Modified AGI>$100,000 (Single), >$200,000 (Joint)
Child Tax Credit:
-Maximum Credit: $2,200 per qualifying child.
-Starting in 2026, it will be indexed for inflation.
Additional Standard Deduction for Seniors (2025-2028)
-Additional standard deduction Seniors (age 65+)
-$6,000 (Single), $12,000 (Joint)
-Phase-Out: Modified AGI>$75,000 (Single), >$150,000 (Joint)
Trump Accounts
-Individual retirement for individuals under 18 years old
-Maximum annual contribution: $5,000 adjusted for inflation starting 2028
-A Pilot Program will provide a tax credit of $1,000 for establishing a Trump Accocunt for children born between January 1, 2025 and December 31, 2028.
-Employers may contribute to Trump Accounts under a Trump Account Contribution Program: This would be a benefit the employer may offer their employees. This money is excluded from the employee's gross income. Maximum annual contribution: $2,500.
Qualified Tuition Programs
-Additional expenses treated as Qualified Higher Education expenses for purposes of 529 Accounts. Treatment of Elementary and Secondary Tuition.
-Increase in maximum annual distribution to $20,000 per eligible student
Permanent Eliminations
Residential Clean Energy Credit: The 30% credit for installing residential renewable energy systems like solar panels expires for expenditures made after 12/31/2025.
Energy Efficient Home Improvement Credit: Expires for property placed in service after 12/31/2025.
New and Used Clean Vehicle Credits: Expires for vehicles acquired after 9/30/2025.
Alternative Fuel Refueling Property Credit: The credit for charging or refueling equipment at their home will expire for property placed in service after 6/30/2026.
*MAGI-Modified Adjusted Gross Income
Estates
Estate, gift, and generation-skipping tax exemptions increased to $15M per person and $30M per couple, post 2025, adjusted for inflation.
Businesses
Permanent Business Tax Incentives*
QBI Deduction:
-The 20% Qualified Business Income deduction is now permanent for pass through entities.
-Income Threshold: $75,000 (Single), $150,000 (Joint)
-Minimum Deduction: $400
Business Meals:
Section 274 of the IRC will preserve the 100% deduction of employer expenses for providing meals or subsidized meals in company cafeterias. Meals provided to employees who cannot obtain a meal during a reasonable period of time: doctors, nurses, or employees at remote work sites, when those meals are excluded from income under Section 119. Under the previous TCJA, these deductions were set to be disallowed starting January 1, 2026.
Bonus Depreciation and Section 179
-100% Bonus Depreciation for qualified property acquired or placed in service after January 19, 2025
-Section 179 Expensing limit increases to $2.5 million. Phase-Out threshold increased to $4 million for property placed in service after 12/31/2024, subject to limitations
Deduction of Research and Experimental Expenditures
-Immediate expensing in full in the year incurred instead of amortizing
-Retroactive to 2022 for small businesses.
-Tax relief for technology, pharmaceuticals and manufacturing companies.
Interest Deduction
Under the TCJA, the deduction of business interest expense was limited to 30% of Adjusted Taxable Income (2022-2025) was based on Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization (EBITDA).
Under the OBBBA:
-Businesses may deduct 100% of business interest expenses in the year incurred, subject to rules.
-Retroactive application: tax years beginning after 12/31/2017. Businesses may claim full deductions for interest expenses from 2018 through 2025 and beyond, if they meet requirements.
Qualified Opportunity Zones (QOZ)
-This incentive program is made permanent with a new rolling 10-year designation process starting mid-2026.
-Extends the deadline to invest capital gains into a Qualified Opportunity Fund from 12/31/2026 to 12/31/2028.
-Investors may defer capital gains tax and receive permanent basis step-ups, including a 30% basis increase for rural fund investments.
QSBS Exclusion (Permanent)
-Phased increased in exclusion for Gain from Qualified Small Business Stock
-Applies to QSBS acquired after July 4, 2025
-50% Exclusion if held 3 years or more
-75% Exclusion if held 4 years or more
-100% Exclusion if held 5 years or more
-Gain exclusion cap: Increased to $15M and asset threshold increased to $75M, both inflation-adjusted.
Employer-Provided Child Care Credit
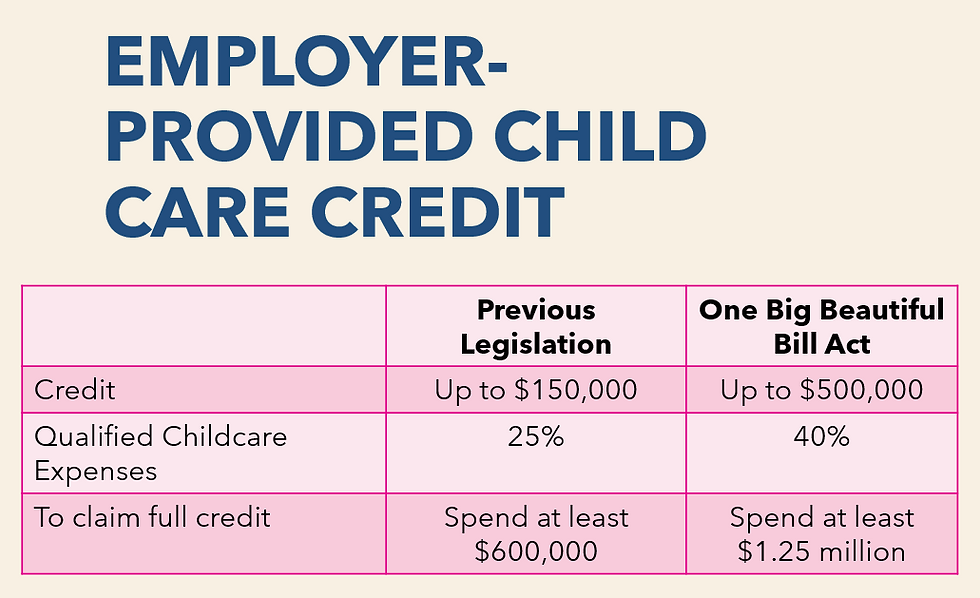
Paid Family and Medical Leave Credit for Employer (Permanent)
Extension of this credit created by the TCJA was set to expire in 2025.
Expands eligibility for the credit by requiring employees to be only 6
months with an employer.
Employees must work a minimum of 20 hours per week.
Employers may choose between 2 methods for calculation:
Wages Paid Method or the Insurance Premium Method.
Employers in state mandating the this leave can receive a federal credit for any paid leave they provide that exceeds the amount required by state or local law.
Credit: 12.5% of qualified wages if employer pays at least 50% of the employee's normal wages. The rate increases up to a maximum of 25% of qualified leave wages, if the employer pays 100% of the normal wages.
Limit: Credit for up to 12 weeks of leave per employee.
Covid-Related Employee Retention Credits (ERTC)
-ERTC claims for 3rd Quarter and 4th Quarter of 2021 filed after 1/31/2024 are not allowed.
-Claims for these quarters that were filed before 1/31/2024 will be processed.
-Statute of Limitation: 6 years from the filing date for the IRS to audit ERTC claims corresponding to the 3rd Quarter and 4th Quarter of year 2021.
The Base Erosion and Anti-Abuse Tax (BEAT) Rate
-This is a minimum tax targeting large U.S. corporations that make significant deductible payments to related foreign parties to erode their U.S. tax base (interest, royalties, service fees, etc.)
-Previously, this tax rate was scheduled to increase gradually from 10% to 12.5% in 2026, then to 15% in 2027 for most taxpayers.
-This Act locks the rate at 10.5% for tax years beginning after 12/31/2025
*These incentives provide for long-term tax planning benefits for qualifying businesses.
Repeal and Phase-Out of Clean Energy Credits
Clean Energy Tax Credits for Business
-Wind and Solar Credits: Production and Investment tax credits are
eliminated for solar and wind facilities placed in service after 12/31/2027.
Deadline waived for facilities beginning construction by July 4, 2026.
-Advanced Manufacturing Production Credit: Modified eligibility criteria.
a.Wind energy components are no longer eligible after 2027.
b.Critical minerals phase-out schedule is introduced for most between
2031-2033.
c. Metallurgical Coal: this was added as a qualifying critical mineral, whith
its credit expiring after 2029.
b. Alternative Fuel Vehicle Refueling Property Credit: eliminated for any property placed in service after 6/30/2026.
c. Commercial Clean Vehicle Credit: elminiated for vehicles purchased after 9/30/2025.
d. Energy Efficient Commercial Building Deduction: not allowed for properties where construction begins after 6/30/2026.
Legacy Credits: Terminates the 2% energy credit under Section 48 for construction projects beginning after 6/16/2025, effectively eliminating the credit for most new projects.
Widespread Tax Reductions Shadowed by Cuts
This Bill delivers sweeping tax reliefs, estimated to cut federal revenue by trillions of dollars, funded largely through cuts to Medicaid, SNAP, CHIP, and other social programs, repeal and phase-out of clean energy tax credits, and government spending cuts across agencies.
Impact of Major Spending Cuts
•Medicaid and CHIP reduction to approximately $1 trillion over the next decade. Rural hospitals will be impacted and may lead to closures or service cuts.
•SNAP (Food Assistance) will have a reduction in $186 billion in funds. May have impact on millions of individuals, including children.
•Clean Energy Tax Credit Changes include accelerated phase-outs, residential credit eliminations, stricter eligibility rules, transferability restrictions and termination of grant programs.
•ACA Premium Tax Credit Rollback – End of enhanced marketplace subsidies. May lead to more uninsured individuals.



Comments